Structured Text Block
Structured blocks store data in structured formats (i.e., JSON Objects or Lists). They're ideal for complex inputs, outputs, or intermediate data passed through processing nodes.
Key features:
- Stores nested structured data that can be navigated via keys or indexes.
- Supports creating multiple views for the same content, with different arrangements.
Examples:
- JSON Object:
{ "name": "Alice", "role": "Manager" } - JSON Array:
[ {"id": 1, "item": "pen"}, {"id": 2, "item": "book"} ]
All views follow a unified JSON format with two fields:
content: The semantic coremetadata: Extra info to guide downstream tasks
Loop Mode:
Loop Mode:
-
What is Loop Mode? Loop Mode enables concurrent processing of each element inside a structured block. It is ideal when the structured content contains multiple items (e.g., a list of records) and you want the connected edge to process each item individually. When enabled, the edge execution will iterate over each element of the block content.
-
Why we use Loop Mode?:Useful for edge types (like LLM) that have context-length limitations or cannot handle large input sizes.
-
This mode is disabled by default and must be toggled manually when needed.
Index Management:
Index Management:
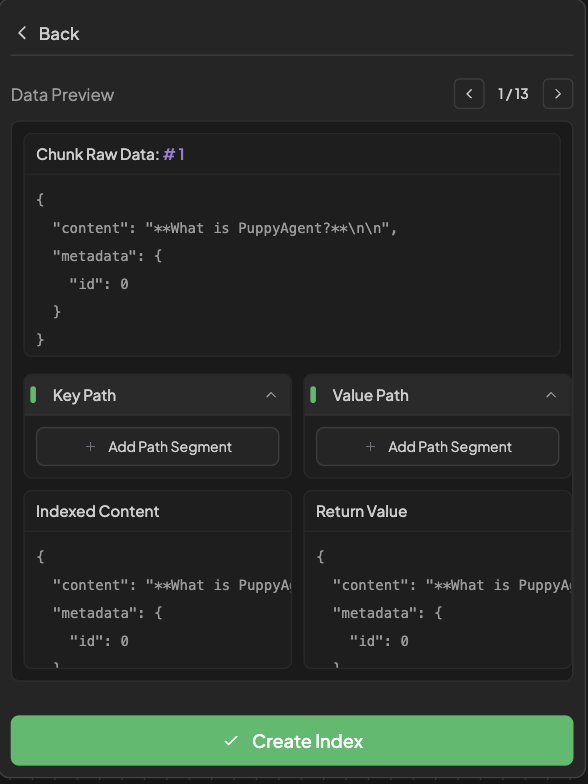
- Used to prepare content for embedding by isolating the semantic content and attaching meaningful metadata.
- Clicking
Add New Indexbutton to create a new Index. - Data Preview Contains
contentandmetadata. - Key Path: Press
Add Path Segmentand enter the fields(contentormetadata)you want to be indexed.- You must add a path segment.
- Value Path: Press
Add Path Segmentand enter the fields(contentormetadata)you want to be matched.- Default: Return whole chunk contains
contentandmetadata.
- Default: Return whole chunk contains
- Tips: You can't edit your index, but you can create a new index to replace it.